![]()
![]()
Linux Patch Management module scans and assesses the patches that are deployed or missing in the Linux systems in the network. This helps make sure that all the Linux systems on the network are up to date with the critical or recent patches that are released for the Linux version and there are no security vulnerabilities in the network. The following sections provide details on configuring settings for scanning the network for missing patches and deploying the same.
Click the 'Settings' tab. In the 'Software Management' section, click 'Patch Management Wizard'. This will list the current patch configurations that are defined if any.
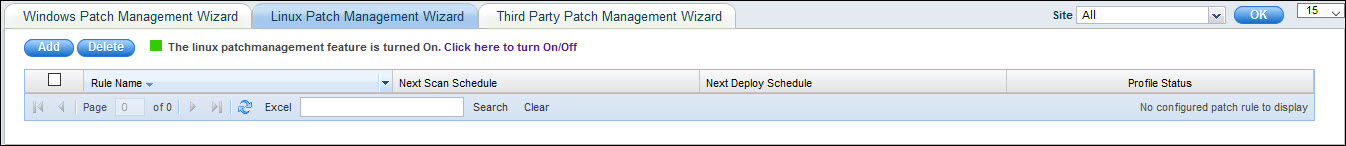
Click on the link to turn the feature on and off. The indicator shows if the feature is active.
To add a new patch configuration, in the 'Linux Patch Management Wizard' tab, click the ‘Add’ button. The first step is to select the hosts that are to be included as part of the patch configuration. You can select an inclusion profile that is created or create a new profile using the ‘Add New Profile’ button. Make sure you select a correct profile.
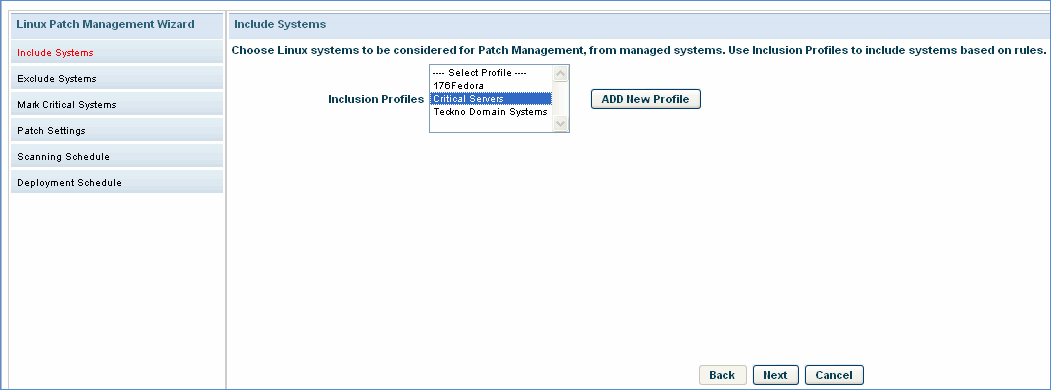
Click 'Next'.
Exclude Systems: The next step is to select the exclusion profile. Devices which are part of this profile will be excluded from the patch scanning activity. In case there are no exclusion profiles click 'ADD New profile' button to add an exclusion profile
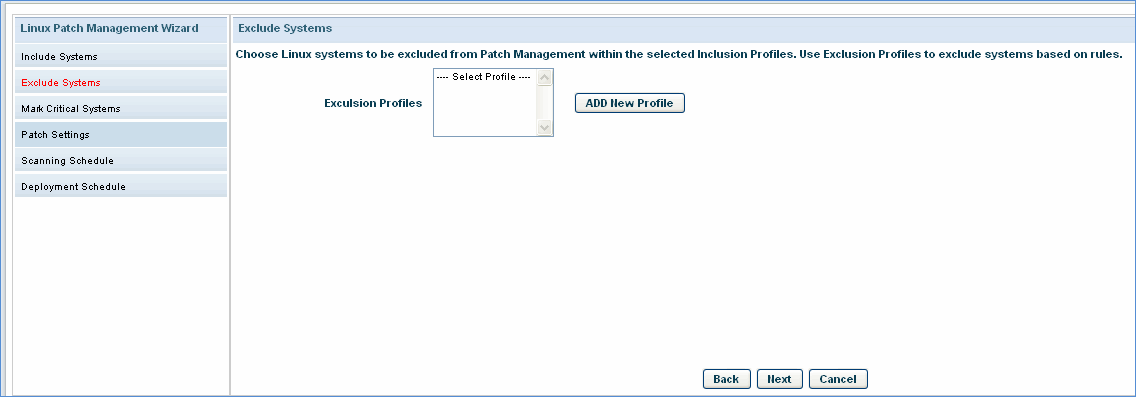
Click 'Next'.
Mark Critical Systems: You can select the profile to define the critical systems. For devices which are marked as critical systems, the patch deployment will always be only on approval.
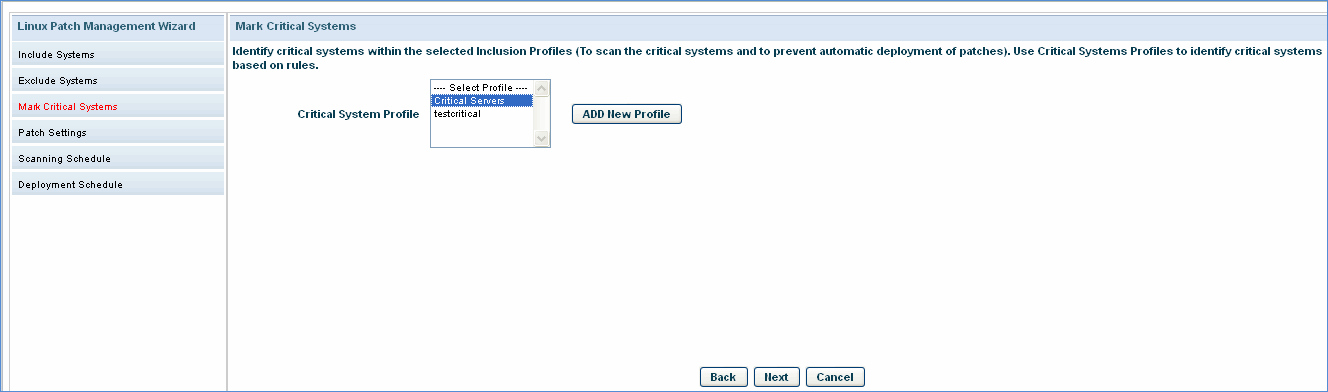
Click 'Next'.
Patch Scan and Deploy Settings: Specify the parameters for patch scan and patch deploy
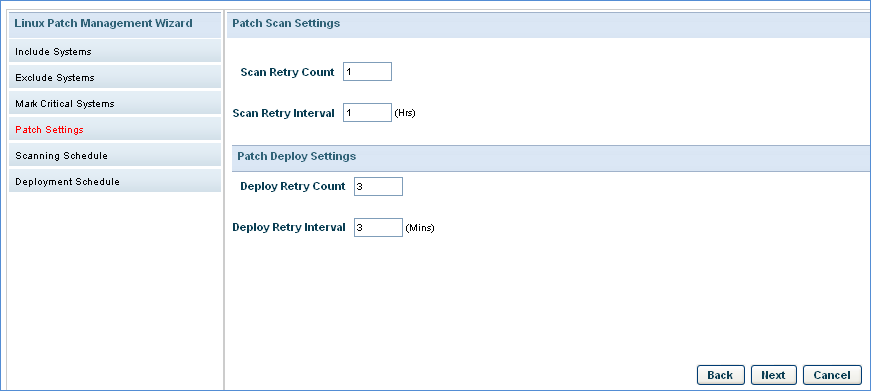
|
Click 'Next'.
Scheduling Patch Scan. Select the schedule interval as per your choice. The devices part of the rule will be scanned only as per the schedule mentioned here.
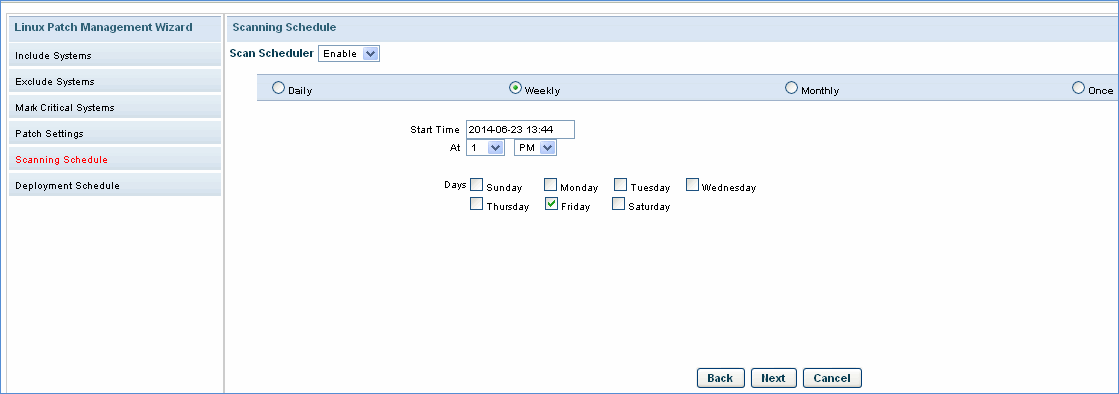
Scheduling Patch Deploy. Select the schedule interval as per your choice. The patch deployment will be attempted only during the time interval that is selected here.
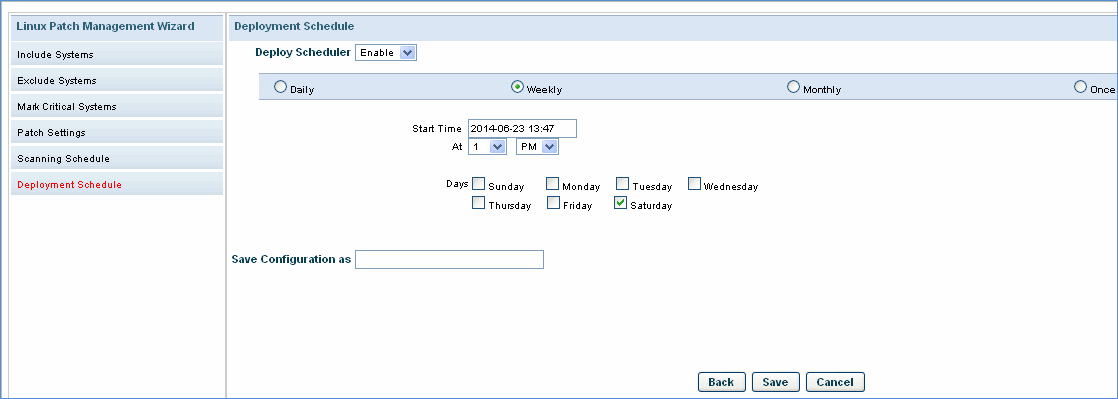
Select the Deployment Schedule. Enter a name in 'Save Configuration As' field. Click on 'Save'.
 Notes:
1. Patch deployment will be performed only when the ‘Deploy Scheduler’
is enabled. Patch deployment will not be performed automatically or on
demand.
Notes:
1. Patch deployment will be performed only when the ‘Deploy Scheduler’
is enabled. Patch deployment will not be performed automatically or on
demand.
2. Even if an automatic patch deployment is enabled, for devices listed in the critical system profile, the deployment will only happen for manually approved patches.