![]()
![]()
For an organization, it is important to manage their software assets efficiently and to avoid the risk of license non-compliance. Software metering makes this easier by giving the usage statistics of software in the network. Software metering also gives the frequency of software usage and unused software on the network which will help IT Managers decide on their organization’s software need of license renewal. The IT engineer can get an e-mail alert when any new unused software is detected on the network and unused software can be uninstalled manually or automatically. IT can also make use of software metering reports to view the software usage in the organization.
With SapphireIMS software metering capabilities, you can:
- Register windows devices with software for monitoring software usage
- Determine how often (and by whom) specific applications are being used
- Identify unused and under utilized licenses
Note: Software metering is only supported on Windows systems
Pre-requisite for software metering
Please check that the user/group provided to discover hardware in SapphireIMS is added in 'Local Security Policy' of the end user target machine. To add users, perform the following steps:
Go to Start > Run > secpol.msc
In the left side panel, expand 'Local Policies'
Select 'User Rights Assignment'
In the right panel, double click 'Debug Programs'
In the popup window, click 'Add User or Group' and add the corresponding user or group used for SapphireIMS discovery
Software Metering Policy
Click the Settings tab. In the Asset and Inventory Management section, click Software Metering
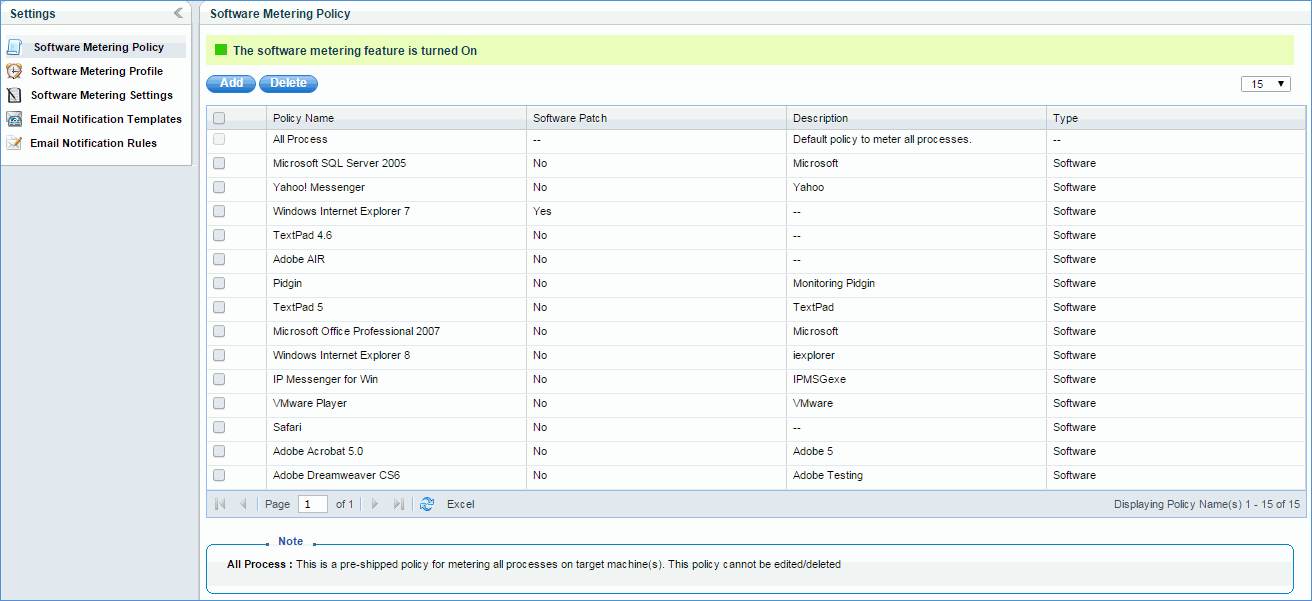
In this page, all created policies are listed including pre-shipped policy “All Process”. Here “All Process” policy is just a rule to meter all processes. It does not mean that it meters all processes on all machines. If the user wants to meter all processes on all machines, he has to create a software metering profile by mapping all systems to this policy.
Add Software Metering Policy
Click 'Add' to add a new monitoring policy
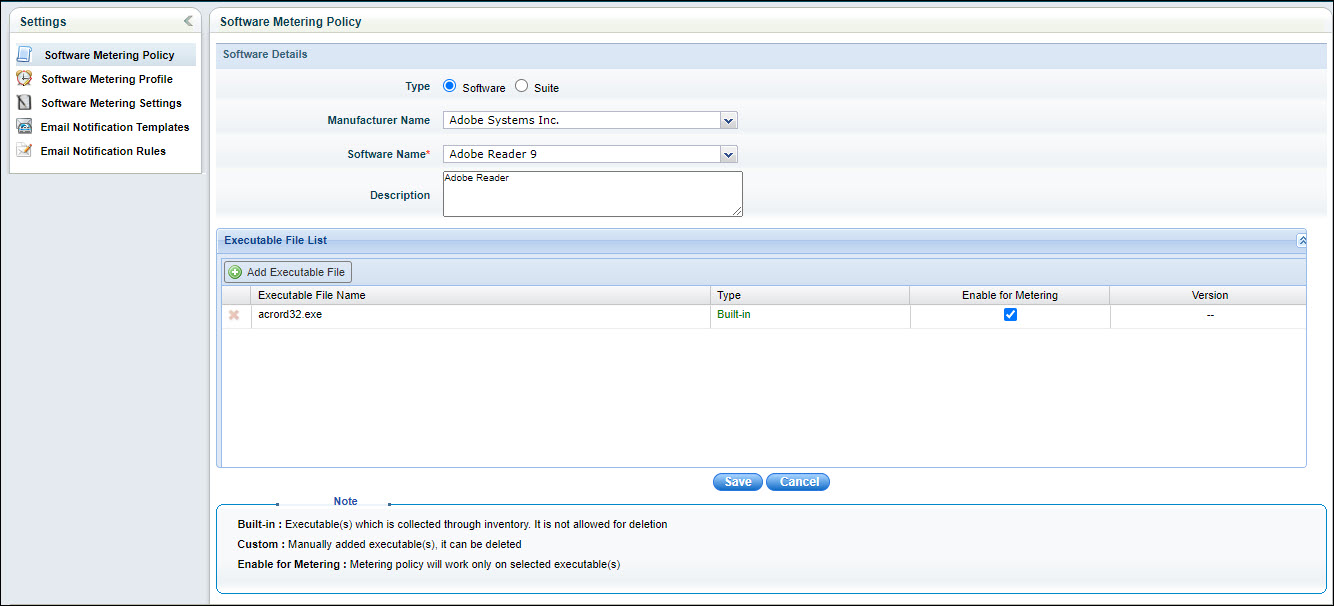
In this page, the user can select a particular suite or software for metering. If a suite is selected, it lists executables related to its components also. Executables listed here are collected as part of inventory. If some executable is not collected as part of inventory, the user can add a custom executable by clicking 'Add Executable File'.
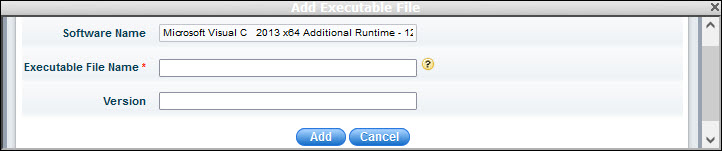
Version is one of the file properties of the executable. This can be found by viewing the properties of the executable.
Software Metering Profile
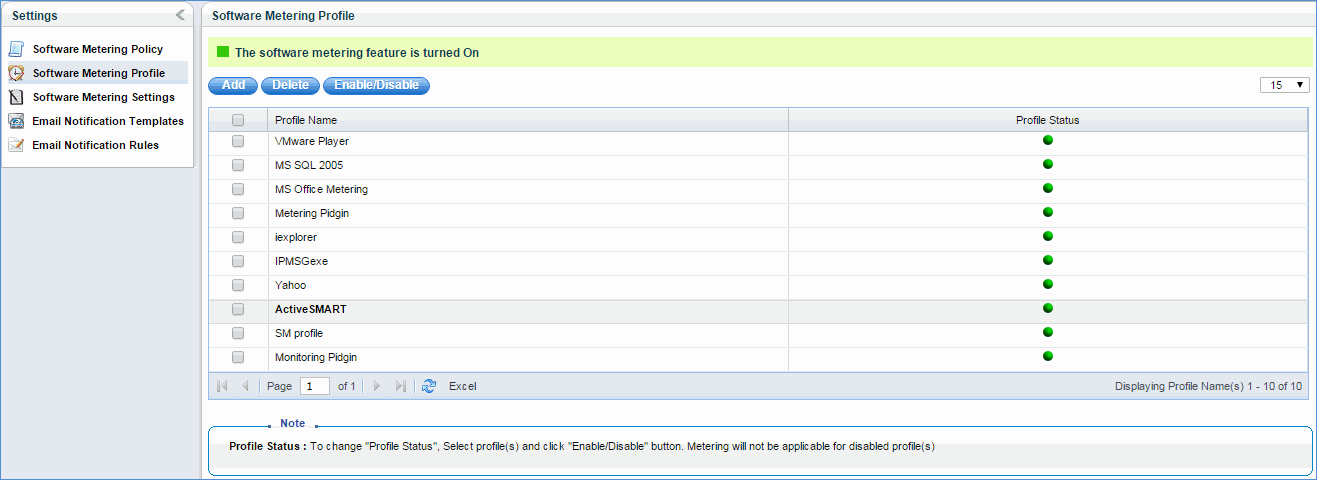
In this page all software metering profiles created by the user are displayed. The user can enable/disable a particular profile. “Profile Status” displays whether the profile is enabled/disabled.
Click 'Add' to add a new software metering profile
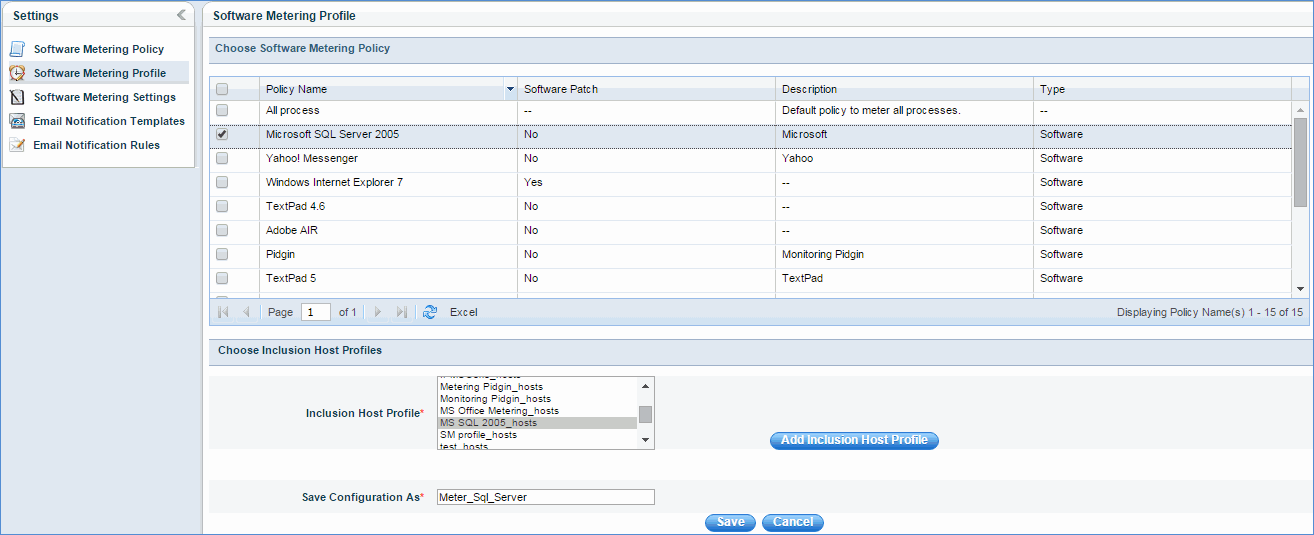
Select metering policies and map them to 'Inclusion Host Profile'. You can add a new host profile by clicking 'Add Inclusion Host Profile' or go to Settings -> Software Management -> Profile Manager -> Generic Host Profile.
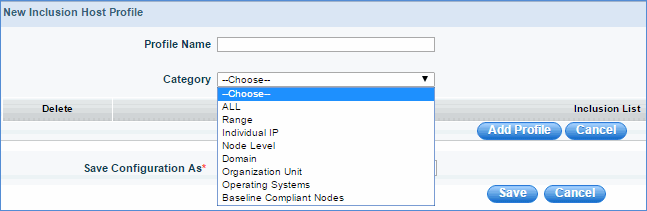
You can select one of the following categories given in the above figure
Software Metering Settings
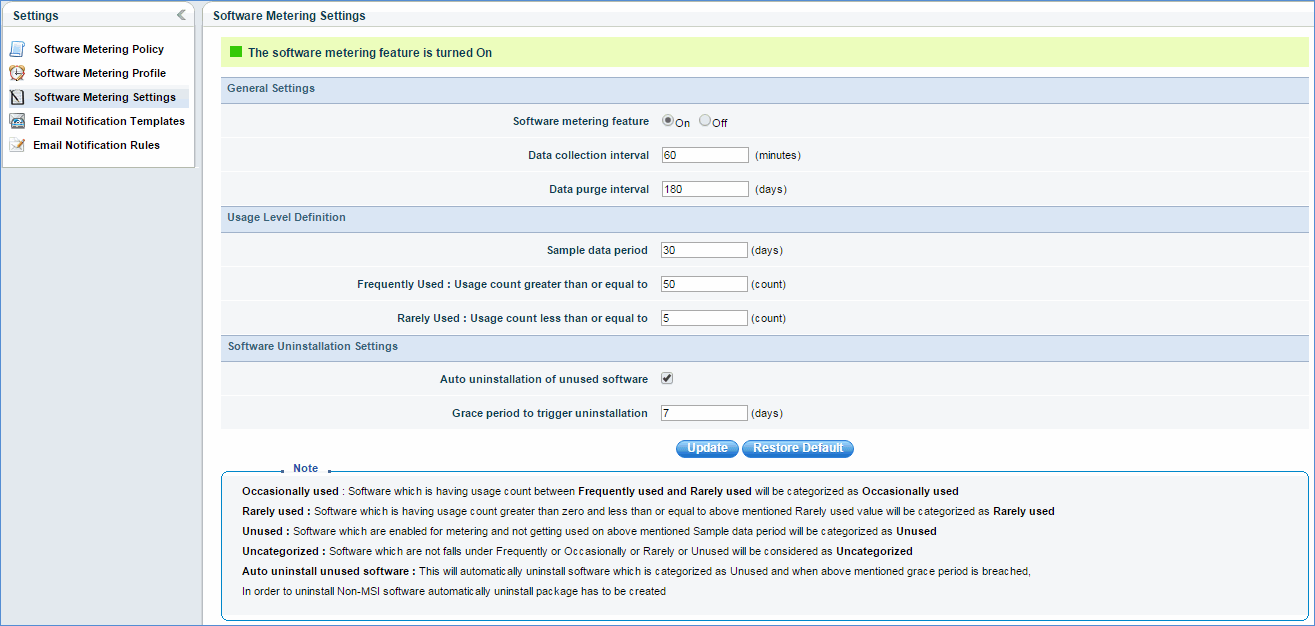
General Settings :
Software metering feature : The user can enable or disable software metering feature. By default it is enabled.
Data collection interval : The interval in which software metering data is to be collected.
Data purge interval : The number of days the software metering data has to be retained in the database.
Usage Level Definition :
Sample data period : Time period to be considered for categorizing software to either Frequently or Occasionally or Rarely or Unused. Software is not categorized until the duration of the sample data period.
Frequently used : Minimum usage count to categorize a particular software as frequently used within the sample data period.
Rarely used : Maximum usage count to categorize a particular software as rarely used within the sample period. This value should be less than the frequently used value and greater than 0.
Software with usage level 0 is classified as Unused. Software usage level between Frequently Used Count and Rarely Used Count is classified as Occasionally used.
Software Uninstallation Settings :
Auto uninstallation of unused software : Once unused software is detected in the network, the user can either manually or automatically uninstall that unused software. To uninstall software automatically, 'Auto uninstallation of unused software' setting has to be enabled and if software is Non-MSI, then a package has to be created.
Grace period to trigger uninstallation : If auto uninstallation is enabled, then the end user is given a grace period to use the software. If the unused software is not used during the grace period, then automatic uninstallation is triggered. If the user uses the software during the grace period, then uninstallation does not happen for the corresponding software on the corresponding host.
Email Notification Templates
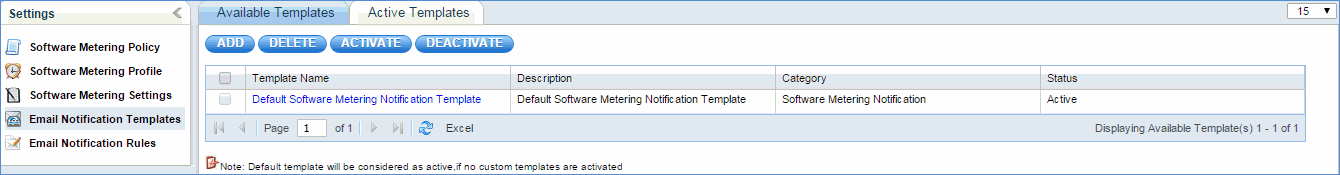
Email notification is used to alert the customer about unused software information on the network. You can edit the pre-shipped e-mail notification template or create your own template. But only one template can be active at a time.
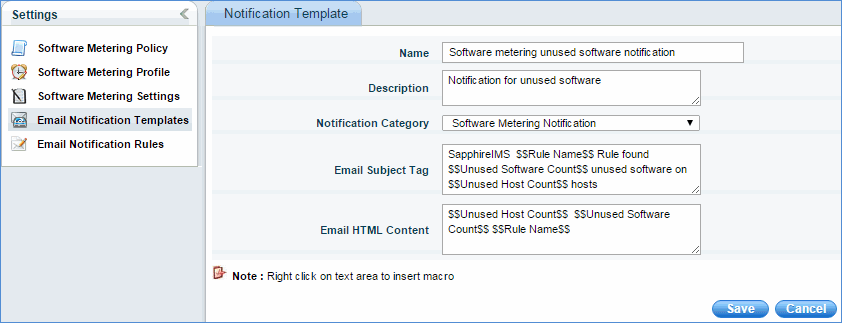
You can add your own e-mail notification template as given above. The above template screen is similar to BSM notification templates or you can create notification template in Settings -> Fault and Notifications -> Notification Templates -> Add -> Software Metering Notification. Here you can define the mail subject and mail content.
Following macros are used
1. Rule Name – Name of the rule for which notification has to be sent.
2. Unused Software Count – Number of unused software found according to a particular rule.
3. Unused Software Count – Number of machines, the above unused software found.
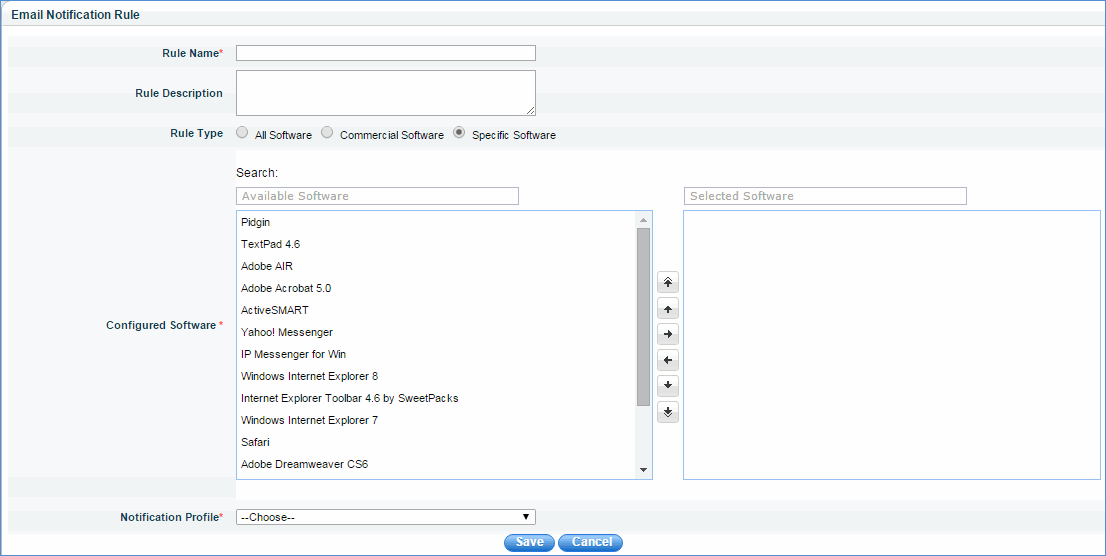
Email Notification Rules
Email notification rules define the conditions to send software notifications for unused software. Click the 'Add' button to define a rule
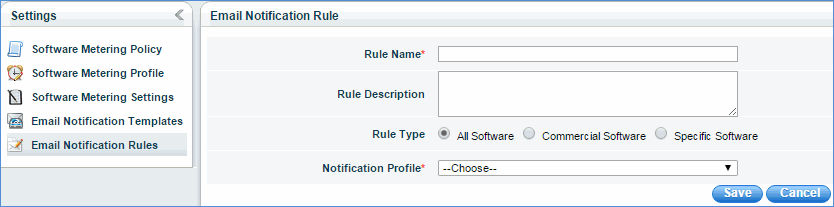
Rule name is a distinct name for a rule which is used as a macro in an e-mail template.
Rule Type:
1. All Software – If a rule is created by selecting All Software, Unused Software Count (Macro) includes all unused software and the corresponding system count is considered as Unused System Count (Macro).
2. Commercial Software – If a rule is created by selecting Commercial Software, Unused Software Count (Macro) includes only commercial software among all unused software. The corresponding system count is considered as Unused System Count (Macro).
3. Specific Software – If you select a specific software, you can choose for which software you want to get notification. Selected software are considered for macro calculation. In the mail, you do not get detailed description of software name and host count. Only consolidated count is sent in the mail. This is a limitation in Software Metering Email Notification.